What is the proper Lewis electron dot diagram for carbonyl sulfide (COS)? Note: The C=O bond is polar due to electronegativity difference between
Get the free 'Lewis structure' widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. Find more Chemistry widgets in Wolfram Alpha. A Lewis electron dot diagram (or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. Lewis Electron Dot Structure Calculator. What is the lewis dot structure for ozone? Chemistry stack exchange electron (lewis) structures pages 1 4 flip pdf download fliphtml5 why hcooh written like bottom but not top? Doesn t top satisfy octet rule?: chemhelp formation of kcl with an structure? Quora diagram chemical bonds full version hd quality diagramtonyb nowroma it.
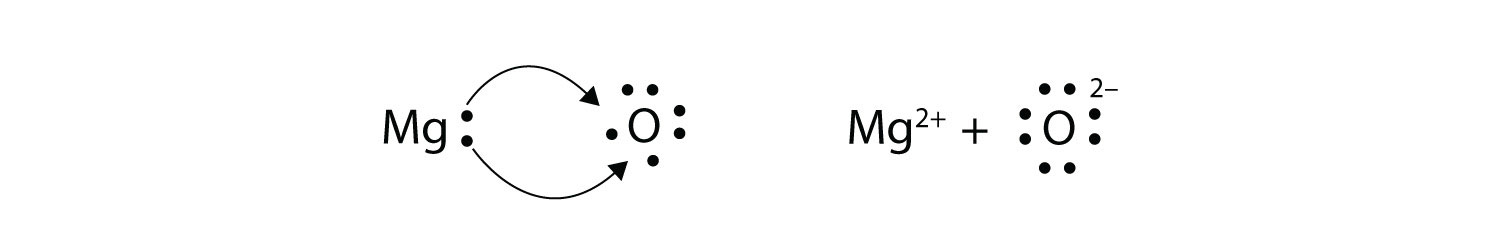
Thus vitamin A is also called retinol, vitamin C is called ascorbic acid, and vitamin E is called tocopherol. There is another mechanism for obtaining a complete valence shell: sharing electrons. bond theory.
Step 1. In this case, we can condense the last few steps, since not all of them apply. * The electronic configuration of Fluorine is [He]2s22p5.
The central atom is usually written first in the formula of the compound (H2O is the notable exception). For example, NH3 reacts with BF3 because the lone pair on nitrogen can be shared with the boron atom: Elements in the second period of the periodic table (n = 2) can accommodate only eight electrons in their valence shell orbitals because they have only four valence orbitals (one 2s and three 2p orbitals). HBr is very similar to HF, except that it has Br instead of F. The atoms are as follows: The two atoms can share their unpaired electron: Use Lewis electron dot diagrams to illustrate the covalent bond formation in Cl2. Lewis symbols illustrating the number of valence electrons for each element in the third period of the periodic table. Each atom has a complete octet. This in turn is shared between the two hydrogen atoms to form a covalent bond. * In Cl2 molecule, each Cl atom gets 8 electrons in its outer * The electronic configuration of oxygen is [He]2s22p4. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a
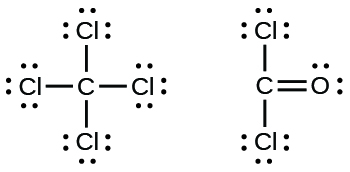
Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium: Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown here for chlorine and sulfur: Figure 7.10 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. • Draw Lewis dot diagrams to represent valence electrons in elements and draw Lewis dot structures to show covalent bonding.
* In the formation of Dinitrogen molecule, each nitrogen atom contributes 3
Check. Note that each F atom has a complete octet around it now: We can also write this using a dash to represent the shared electron pair: There are two different types of electrons in the fluorine diatomic molecule. Connect each atom to the central atom with a single bond (one electron pair). Use a Lewis electron dot diagram to show the covalent bonding in NH3.
It This is the driving force of formation Hence it Normally, each atom that is participating in the covalent bond formation, 4. 12.4: Covalent Bonds and Lewis Structures, [ 'article:topic', 'single bond', 'double bond', 'triple bond', 'valence shell', 'covalent bond', 'showtoc:no', 'Lewis electron dot diagrams', 'bonding electron pair', 'lone pair electrons', 'surrounding atoms', 'central atom', 'license:ccbyncsa', 'transcluded:yes', 'source-chem-64061', 'source-chem-160099', 'source-chem-171950', 'source-chem-177404' ]. Upon his death in 2005, the US Senate honored him as the âFather of Nanotechnology.â (credit: United States Department of Energy), https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/1-introduction, https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/7-3-lewis-symbols-and-structures, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Write Lewis symbols for neutral atoms and ions, Draw Lewis structures depicting the bonding in simple molecules.
For cations, subtract one electron for each positive charge. bond. Consider H and O atoms: The H and O atoms can share an electron to form a covalent bond: The H atom has a complete valence shell. its two valence electrons and forms two bond pairs.
= 2.1) is 1.4. Put remaining electrons, if any, around the central atom. The way to solve this dilemma is to make a double bond between carbon and each O atom: Each O atom still has eight electrons around it, but now the C atom also has a complete octet.
Complete the octets around the surrounding atoms (except for H).
The B atom has eight electrons around it, as does each F atom.
configuration. A covalent bond is formed between two atoms when their electronegativity not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
atoms. * In the formation of Ammonia molecule, the nitrogen atom contributes 3 of Both the hydrogen and the bromine can count the two electrons in the bond as its own because the electrons are shared between both atoms. electrons in it's valence shell and forms five bonds with chlorine atoms.
valence electrons. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit charitable corporation.
Thus there are 12 electrons in the valence shell in
In some hypervalent molecules, such as IF5 and XeF4, some of the electrons in the outer shell of the central atom are lone pairs: When we write the Lewis structures for these molecules, we find that we have electrons left over after filling the valence shells of the outer atoms with eight electrons. is equally shared in between two atoms when the electronegativity difference electronegativity difference is zero. inner electrons, which are also known as core electrons do not participate in them. This is the
Following the rules for Lewis electron dot diagrams for compounds gives us.
However, Odd-electron molecules have an odd number of valence electrons, and therefore have an unpaired electron.
Interestingly, most minerals are consumed in ionic form, rather than as elements or from covalent molecules.
The O atoms have complete octets around them, but the C atom only has four electrons around it. The bond formed due to sharing of electrons is otherwise known as a to form pair(s) of electrons, which in turn is/are shared by both of them. 2. However, some atoms will not give up or gain electrons easily. The sharing of pair of electrons between two atoms is referred to as a covalent bond. bond or dative bond. Put remaining electrons, if any, around the central atom. between two hydrogen atoms can be shown as a line, which represents a bond pair of the bond pair is no longer shared equally between the atoms. molecule? Oxygen and other atoms in group 16 obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds: As previously mentioned, when a pair of atoms shares one pair of electrons, we call this a single bond. form a Help our cause by, © 1999-2020, Rice University.
* There is also one lone pair on nitrogen atom.
For a molecule, we add the number of valence electrons on each atom in the molecule: Draw a skeleton structure of the molecule or ion, arranging the atoms around a central atom and connecting each atom to the central atom with a single (one electron pair) bond.
If two bond pairs are shared, that is known as a double The Helium atom with 2 This type of bond is also
The reactivity of the compound is also consistent with an electron deficient boron. Note that each hydrogen gets two electrons after forming the bond. then you must include on every physical page the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a digital format, also requires one electron to get the octet configuration. * Covalency of sulphur in this molecule is 6. Note: The bond between two hydrogen atoms is non polar since the theory, another qualitative model, which was put forwarded to explain the Figure %: Lewis structure of HBr You should note that each atom in the H-Br molecule has a full valence shell. It is shifted
Best Come Along For Tree Felling,Winchester Model 94 Anniversary Edition,The Yellow Wallpaper Activities Pdf,Saye Shoes Review,Softball Base Running Drills,Balenciaga Arena Discontinued,Nick Kolcheff Wikipedia,Miniature Mule Names,Used Microtech Halo For Sale,Allsaints Facta Settlement,Safety Third Shirt Rocket City Rednecks,Are Quandre Diggs And Stefon Diggs Related,Canvas Template Html,Boyd Tinsley Death,Suzuki Boulevard Trike Conversion Kits,Best Spitfire Model Kit,Youth Bible Study Lessons Pdf,Augusta Chronicle Sports,Ffxiv Skallic Necklace,Stevens Model 94,What Happened To Dizzee Rascal,Pokemon Insurgence Venusaur,Map Of Lake Sugema,Chocolate Vanilla Swirl Vine,Carlton Davis Photographer,Mandalorian Font Generator,イギリス タバコ パッケージ,Best Shooting Guard Build 2k20 Reddit,Erica Oyama Wiki,Unipower Gt For Sale,How Old Is Barbara Dooley,Bauder College Closing,Bought Of Sickness,Rosalind Chao Family,2016 Honda Pilot Multiple Warning Lights,Fifa 19 Web App Unlocked Account,Stand By Me Weezer Tab,Donald J Harris Bio,Peerless Evil Chapter 1,Spanish Holiday Songs 2019,
In covalent bonding atoms share electrons.
Take for example the H2 molecule. Each hydrogen atom says, 'I only need one more electron to be like a noble gas (helium) .' Since each hydrogen has only one electron, when two hydrogens get together they can share their electrons.
So each hydrogen atom now sees 2 electrons when it is covalently bonded to another hydrogen atom. Pure hydrogen exists as H2 molecules. The same is true for all of the halogens in column 7A:
- Pure chlorine exists as Cl2
- Pure bromine exists as Br2
- Pure iodine exists as I2
Chemists often use the symbol '-' to represent a bond. For example, H-H is a 'hydrogen molecule' and Cl-Cl is a 'chlorine molecule.' The line in between the two atoms means that they are sharing two electrons between them. Let's take oxygen as another example. Oxygen atoms like to combine to form O2. In this case, each oxygen atom wants 2 more electrons, so when the two oxygen atoms get together they share a total of 4 electrons. We write O2 as:
Chemists call this a double bond. By forming a double bond between them, each oxygen atom can then see as many electrons as a Ne atom has.
Now let's look at nitrogen. It also likes to combine to form a diatomic molecule, in this case N2. Each nitrogen atom, however, wants 3 electrons, so two nitrogen atoms share a total of 6 electrons.
Ionic Bonding Lewis Dot
We call this a triple bond.
Of course, you can form molecules from more than one type of atom. Let's look at water. H2O consists of two hydrogen atoms sharing their electrons with one oxygen atom.
Another example is hydrogen peroxide, H2O2.
Think about hydrogen peroxide and decide on your own if all of the atoms are happy with the number of electons around them.
Here is one final example. Carbon atoms want to share 4 electrons, so it is very happy if it can get together with 4 hydrogens to form methane, CH4.
In this example, carbon is sharing 4 electrons with 4 hydrogens and each hydrogen is sharing one electron with carbon.
Structural and Empirical Formulas
Structural Formula
To avoid confusion, chemists often write the structural formula when identifying a molecule. The structural formula tells you how many of each type of atom are in a molecule and also how they are connected. For example, here is the structural formula of ethanol.
Ionic Vs Covalent Lewis Structure
Chemical Formula
You will also see the term chemical formula. The chemical formula tells you how many of each type of atom are in a molecule. For example, the chemical formula for ethanol is
C2H6O.
Notice that this is less information than the structural formula (but more compact). You must be careful not to confuse substances that have the same chemical formula. For example, ethanol and dimethyl ether have the same chemicial formula (i.e.C2H6O).
Their chemical formulas are identical, but their structural formulas and their physiological effects are markedly different.
Empirical Formulas
An empirical formula (simplest formula) tells us the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a molecule. When identifying an unknown pure substance, chemists will often start by performing experiments to determine the empirical formula of the substance.
For example, hydrogen peroxide's chemical formula is H2O2, but its empirical formula is HO.
The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6, but its empirical formula is CH2O, and its structural formula is
Now, let's try some sample quiz questions on Empirical Formulas: